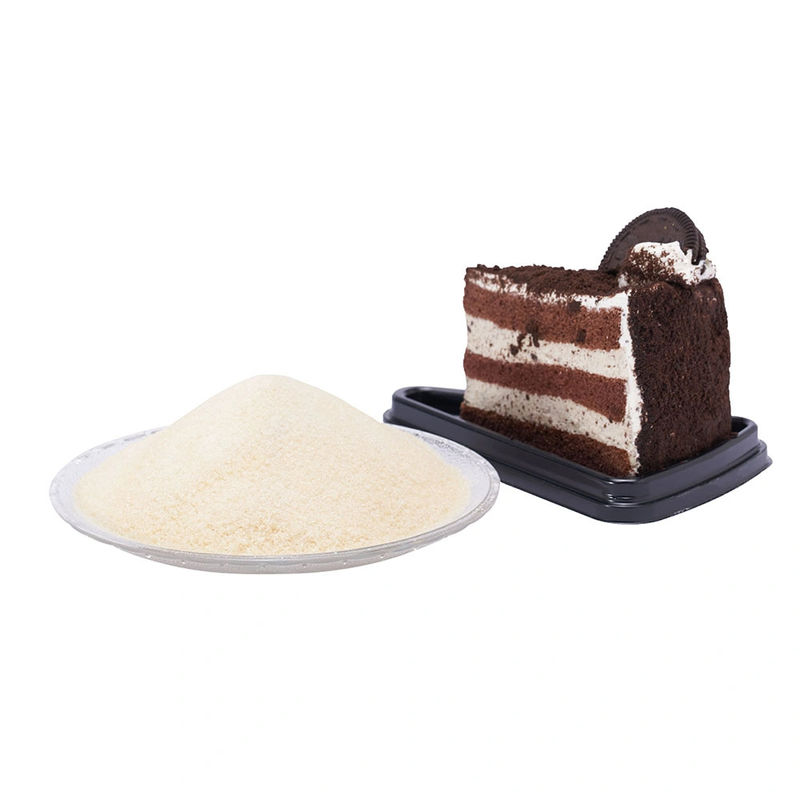
ISO Certified SUNRI Edible Gelatin Powder 95% Protein CAS 9000-70-8
Product introduction
Edible gelatin powder is a protein product of natural origin.
Gelatin powder vary from80 to 260 Bloom grams and, except for specialtyitems, are free of added colors, flavors, preservatives, and chemical additivesGelatin is a generally recognized as safe food gelatin's most desirable propertiesare its melt-in-the-mouth characteristics and its ability to form thermo reversiblegels.Gelatin is a protein made from partial hydrolysis of animal collagen. Food-grade gelatin is used as gelling agent in making jelly, marshmallows and gummycandies. oreover, it is also used as a stabilizing and thickening agent inmanufacturing jams, yoghurt and ice-cream.

Features:
1.Thickening
2.Gelling
3.Water Retention
4.Foaming
5.Emulsifying & Stability
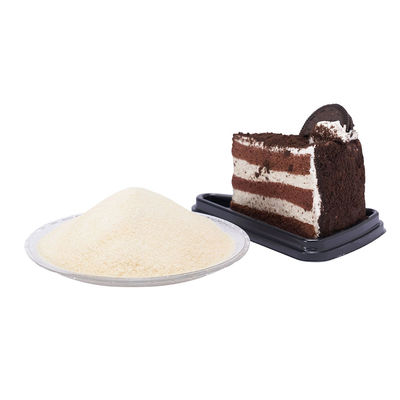
Anchi has a series of edible gelatin which can be widely used in the production of confectionery, dairy, beverage, meat, bakery, desserts, and cooked foods.
NougatGel
MarshmallowGel️
YogurtGel
GummyGel
Edible gelatin powder Application:
Confectionery:
Confections are typically made from a base of sugar, corn syrup, and water. To this base, they are added flavor, color, and texturemodifiers. Gelatin is widely used in confections because it foams, gels, or solidifies into a piece that dissolves slowly or melts inthe mouth.
Confections such as gummy bears contain a relatively high percentage of gelatins. These candies dissolve more slowly thuslengthening the enjoyment of the candy while smoothing the flavor.
Gelatin is used in whipped confections such as marshmallows where it serves to lower the surface tension of the syrup, stabilizethe foam through increased viscosity, set the foam via aelatin, and prevent suaar crvstallization
Gelatin is used in foamed confections at a 2-7% level, depending upon the desired texture. Gummy foams use about 7% of a 200.275 Bloom gelatin. Marshmallow producers generally use 2.5% of a 250 Bloom Type A gelatin
Wine and Juice Fining
By acting as a coagulant, gelatin can be used to precipitate impurities during the manufacture of wine, beer, cider, and juices. ithas the advantages of unlimited shelf life in its dry form, ease of handling, rapid preparation, and briliant clarification

Food gelatin powder product parameters
|
item
|
value
|
|
CAS No.
|
9000-70-8
|
|
Other Names
|
Food gelatin powder
|
|
MF
|
C102H151O39N31
|
|
EINECS No.
|
232-554-6
|
|
Place of Origin
|
China
|
|
Type
|
Emulsifiers, Stabilizers, Sweeteners, THICKENERS
|
|
Brand Name
|
SUNRI
|
|
Model Number
|
Food Gelatin
|
|
Appearance
|
Light Yellow Powder or Granule
|
|
Certification
|
ISO
|
|
Smell
|
odorless, unflavored, natural
|
|
Shelf life
|
3 years
|
|
Grade
|
Food Grade.
|
|
Solubility
|
100% Soluble
|
|
Model Number
|
80~300bloom
|
|
Application
|
Candy,Soft Capsule
|

Company introduction
SUNRI can provide high quality of Bovine gelatin according to the reqruiements of manufacturers.SUNRI 80-320 bloom Bovine gelatin can meet clients'demand of a wide spectrum of functions.
As a reliable suppliers of gelatin,SUNRI provide Bovine gelatin to many top brand food manufacturers in different countries in US, Russia, Philippines, India, UAE and so on. Our Bovine gelatin is 100% from bovine skin, which is the material extracted from the hide of cows and cattles. Bovine gelatin offers functional additives for food industries.
Normally, the gelatin of 80-320 bloom, viscosity 1.0-4.0 mPa.s are widely used in food production. And we can also provide different options of higher bloom and viscosity arrcording to clients'demand. And our Capacity is 15000 tons per year, make sure the your supply chain stable and safety.
Our Halal gelatin have FDA,ISO,HACCP,FSSC,GMP, HALAL certification,can bring safety, health and stable quality to you. And our quality meet the GB,EU,USP standard.And we have rich export experience in many different countries to make sure gelatin can be received smoothly.
Our Package:25KG/Bag,PE bag inside, paper bag outside.
Custom clearance documents: Certificate of Analysis; Veterinary Health certificate; Certificate of Origin.B/L,Packing List and Commercial Invoice
Why Choose SUNRI?
*Quality
*Technical Support (over 20 years industry R&D experience)
*Global Supply Chain
*Competitive Price
*Customers over 60 Countries
*Outstanding Pre-sale and After-sale Service
*Innovative Technology
FAQ
1: what services can we provide?
Accepted Delivery Terms: FOB,CIF,CIP;
Accepted Payment Currency:USD,CNY;
Accepted Payment Type: T/T,L/C,D/P D/A,MoneyGram,Credit Card;
Language Spoken:English,Chinese,Russian
2.What's your payment terms
T/T or L/C.
3.What's your delivery time?
Usually we will arrange the shipment in 7 -15 days.
4.What documents you provide?
Usually, we provide Commerical Invoice, Packing List, Bill of loading, COA , Health certificate and Origin certificate. If your markets have any special requirements, let us know.
5,what can you buy from us?
Gelatin,Industrial Gelatin,Halal Gelatin,Bone Glue,Gelatin Used For Capsule
6.how can we guarantee quality
Always a pre-production sample before mass production;
Always final Inspection before shipment;

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 




