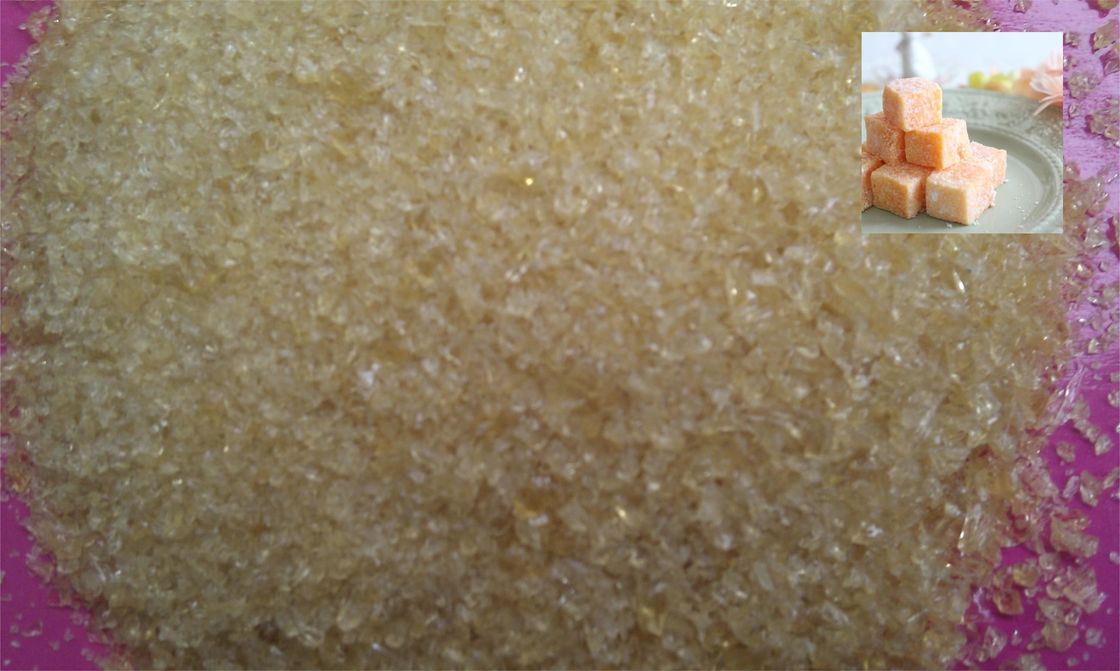
Edible Cattle Skin Gelatin Powder Food Grade Beef Gelatine 80-280bloom
Anchi gelatines, delivered in grain or powder form, is stable during storage provided that it is kept away from heat and moisture, preferably below 35°C (95°F) and below 70% relative humidity.
When stored in the previously mentioned conditions and in its original unopened packaging, Anchi gelatines will maintain their initial properties for at least 2 years.
Handling Directions
Recommendation for dispersion and solubilisation
A proper solubilisation of Anchi gelatines is critical for reaching the complete development of their functionalities. There are four main dissolution methods, allowing the preparation of up to 40% gelatin solution:
Conventional method:
Anchi gelatin is first swelled in cold water (30 minutes to 1 hour) and then dissolved by heating in a water bath
High speed method :
Anchi gelatin is directly dispersed in hot water (80-90°C) with appropriate high-speed stirring. Once dispersed, it will dissolve under slow agitation (5 to 10 minutes)
Intermediate method:
Anchi gelatin is swelled in cold water (30 minutes to 1 hour) and then dissolves by addition to hot ingredients
Dissolution of mixes:
For fine particle size, Anchi gelatin is mixed to other dry ingredient before dissolution
Preserve viscosity and gelatin characteristics
While gelatin is very stable in its gel form, various factors such as pH, temperature or bacterial environment may cause an hydrolysis of the protein chain yielding a decrease in viscosity and Bloom. It is thus very important to protect the solution against elevated temperature and at extreme pH for extended periods of time.
Cleaning Procedures:
Washing the equipment used for processing gelatin based products, is essential for maintaining good hygiene conditions and is easy to perform since gelatin is highly soluble in water.
For a batch process, the cleaning is done by washing, soaking or immersion of the equipment:
· Always start washing with very hot water, at least 80°C, to let swell and solubilize a maximum of residual gelatine
· Then the equipment is cleaned with a 2 to 5% soda solution, maintained at 60-80°C for 30 minutes for a total destruction of organic matters. (This treatment is possible only for stainless steel or glass)
· Finally, an acid treatment with an acid diluted bath (3 to 5‰) at 60 to 80°C will destroy mineral matters if any
· After each alkaline or acid bathes, the equipment is rinsed with hot water and the pH is measured ( to come back to neutrality)
· At last, if bacteriological problems occur, a disinfection of the equipment is possible, with a thermal treatment (steam or boiling water) or chemical treatment (ex sodium hypochlorite at 1 to 2% in concentration) followed by a rinsing step
Recommendations:
· The equipment has to be cleaned as much as possible and usually a daily cleaning is suited
· Cleaning and disinfection are suited after every accidental stop
Disinfection is unnecessary without a previous cleaning procedure

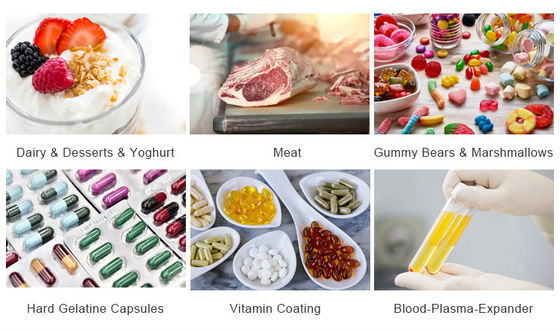
The typical quality and dose of gelatin for each product is given in table.
| Application |
Gel strength
(bloom)
|
High
Viscosity
|
Average
Viscosity
|
Others |
Rate of
Use
|
|
Meat industry
Jellies
|
150-250 |
X |
X |
Transparency colour |
3-15% |
| Binders for meat emulsions |
150-250 |
X |
X |
Transparency |
0.5-3% |
| Hams, canned meat products |
150-250 |
X |
X |
Transparency |
1-2% |
| Coatings |
150-250 |
X |
X |
Transparency |
5-20% |
|
Fish products
Binders
|
150-250 |
X |
X |
Transparency |
0.5-3% |
|
Fish products
Aspics
|
150-250 |
X |
X |
Transparency |
3-15% |
| Sauces, soups |
150-250 |
X |
X |
Transparency colour |
0.5-2% |
Clarification (用途8)
The clarification process consists in adding a substance which can be flocculated and which, will on setting, carry down the suspended particles that produce haze in wine or fruit juice.
Gelatin and Hydrolyzed Gelatin are particularly suited for red wine, beer and apple juice clarification where it reduces turbidity and decreases the astringency of final beverages without negative impact on suitable flavour components.
The gelatin is one of the most frequently used as agent for fining red wines in all wine producing regions.
Among all the products usable for wine clarification, it is the only one which is a food substance of excellent bacteriological quality and which allows:
· an unlimited shelf life in the dry state
· simple handling, especially for those qualities which are soluble in cold water,
· a rapid precipitation of the dense flocs
· bright clear wines without alteration of their color
The use of gelatin for fining white and rosé wines is less systematic, as it nearly always requires the addition of extra tannin in order to coagulate the naturally present protein and so avoid overfining.
Temperature is of main influence:
· cold conditions favours flocculation and clarification. It has been demonstrated that flocculation of wine is difficult at temperature between 25 and 30°C or even impossible at least in white wine
· Temperature between 14 and 16°C are common in wine fining
· High amount of precipitate at lower temperature could be explained by co-precipitation of other components than polyphenol with gelatin or RHC during the process
· Best results are obtained between 10 and 15°C for apple juice, while beers can be fined as low as 1 to 2 °C
A small difference of acidity is enough to affect the fining:
· For wine, the weaker the acidity, the quicker the flocculation
· For apple juice or young wines rich in protective colloids, the influence of acidity is inverted: the more acid the apple juice, the better and more rapid the clarification
· Concerning apples, ripeness and variety of the fruits are of great influence: the ripper the apples, the better the clarification. The more sour the fruit and the lower in tannin, the smaller the amount of gelatine required to get a satisfactory reaction
Overfining (excess of gelatin):
· The main risk is overfining (excess of gelatin), with some factors that favours overfining, as increasing acidity
· Overfining test: when adding a few drops of the tannin solution, there should be no precipitate, but the liquid becomes hazy
· How to proceed when a wine has been overfined: in case where the above test reveals the presence of an excess of gelatin, together with poor fining results, the use of bentonite is recommended to absorb the proteins in excess
Preliminary tests should be made in order to determine the optimum dose of bentonite. This operation must always be followed by either filtering or centrifuging.
FAQ:
1. What's your payment terms?
T/T or L/C.
2. When will i get reply?
We ensure you fast response, fast service .Emails will be replied in 12 hours,your questions will be answered in time
3. How about the packing?
Usually we provide the packing as 25 kg / bag or carton. Of course, if you have special requirements on them, we will according to you.
4. How about the validity of the products?
According to the products you ordered.
5. What documents you provide?
Usually, we provide Commerical Invoice, Packing List, Bill of loading, COA , Health certificate and Origin certificate. If your markets have any special requirements, let us know.
6. What is loading port?
Usually is Shanghai,Qingdao or Tianjin.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!